Cloudify manager worker helm chart ( Premium Version )
Description
It’s a helm chart for cloudify manager which:
- Is highly available, can be deployed with multiple replicas. ( available only when used NFS like Storage file system )
- Uses persistent volume to survive restarts/failures.
- Uses DB (PostgreSQL), which may be deployed as a dependency automatically (also possible to use external postgresql).
- Uses Message Brokers (rabbitMQ), which may be deployed as a dependency automatically.
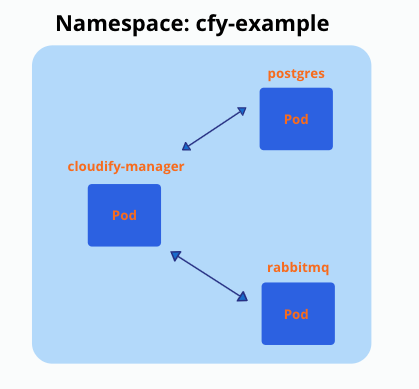
This is how the setup looks after it’s deployed to ‘cfy-example’ namespace (it’s possible to have multiple replicas (pods) of cloudify manager):
Prerequisites
- Docker installed
- Kubectl installed
- Helm installed
- Running Kubernetes cluster (View differences between cloud providers)
- Sufficient Kubernetes node Minimum Requirements
- Cloudify Premium valid license (for Premium version)
How to create and deploy such a setup?
You need to deploy DB and Message Broker before deploying Cloudify manager worker
Generate certificates and add as secret to k8s
SSL certificate must be provided, to secure communications between cloudify manager and posrgress/rabbitmq
-
ca.crt (to sign other certificates)
-
tls.key
-
tls.crt
Option 1: Automatically generate certificates by cert-manager component installed to kubernetes cluster
Cert-manager (https://cert-manager.io) should be previously installed into your k8s cluster for that!
This feature is disabled by default in helm chart, you can enable it if you add to your helm values file:
tls:
certManager:
generate: true
NOTE: Secrets, generated by cert-manager won’t be removed automatically if you uninstall helm release and can be re-used later.
Option 2: Create certificates using the community cloudify manager docker container
$ docker pull cloudifyplatform/community-cloudify-manager-aio:latest
$ docker run --name cfy_manager_local -d --restart unless-stopped --tmpfs /run --tmpfs /run/lock cloudifyplatform/community-cloudify-manager-aio
Exec to the manager and generate certificates
$ docker exec -it cfy_manager_local bash
# NAMESPACE to which cloudify-manager deployed, must be changed accordingly
$ cfy_manager generate-test-cert -s 'cloudify-manager-worker.NAMESPACE.svc.cluster.local,rabbitmq.NAMESPACE.svc.cluster.local,postgres-postgresql.NAMESPACE.svc.cluster.local,localhost'
You can change the name of the created certificates (inside the container):
$ cd /root/.cloudify-test-ca
$ mv cloudify-manager-worker.helm-update.svc.cluster.local.crt tls.crt
$ mv cloudify-manager-worker.helm-update.svc.cluster.local.key ./tls.key
Exit the container and copy the certificates from the container to your working environment:
$ docker cp cfy_manager_local:/root/.cloudify-test-ca/. ./
Create secret in k8s from certificates:
$ kubectl create secret generic cfy-certs --from-file=./tls.crt --from-file=./tls.key --from-file=./ca.crt -n NAMESPACE
Option 3: Use cert-manager component installed to kubernetes cluster (manually)
You need to deploy those manifests, which will generate cfy-certs secret eventually, you need to change NAMESPACE to your namespace before. You can find this manifest in external folder - cert-issuer.yaml
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: Issuer
metadata:
name: selfsigned-issuer
spec:
selfSigned: {}
---
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: Certificate
metadata:
name: cfy-ca
spec:
secretName: cfy-ca-tls
commonName: NAMESPACE.svc.cluster.local
usages:
- server auth
- client auth
isCA: true
duration: "87660h"
issuerRef:
name: selfsigned-issuer
---
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: Issuer
metadata:
name: cfy-ca-issuer
spec:
ca:
secretName: cfy-ca-tls
---
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: Certificate
metadata:
name: cfy-cert
spec:
secretName: cfy-certs
isCA: false
duration: "87660h"
usages:
- server auth
- client auth
dnsNames:
- "postgres-postgresql.NAMESPACE.svc.cluster.local"
- "rabbitmq.NAMESPACE.svc.cluster.local"
- "cloudify-manager-worker.NAMESPACE.svc.cluster.local"
- "postgres-postgresql"
- "rabbitmq"
- "cloudify-manager-worker"
- "localhost"
issuerRef:
name: cfy-ca-issuer
Create a local copy of the cert-issuer.yaml and apply it to the namespace:
$ kubectl apply -f ./cert-issuer.yaml -n NAMESPACE
Clone cloudify-helm repo
This step is necessary because the following steps will require files from this directory
- In case you don’t have Git installed - https://github.com/git-guides/install-git
$ git clone https://github.com/cloudify-cosmo/cloudify-helm.git && cd cloudify-helm
Install cloudify manager worker
Create secret/configMap with premium license - required if using Cloudify premium version
Create license.yaml file and populate it with license data
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: cfy-license
namespace: <NAMESPACE>
data:
cfy_license.yaml: |
license:
capabilities: null
cloudify_version: null
customer_id: <CUSTOMER_ID>
expiration_date: 12/31/2021
license_edition: Premium
trial: false
signature: !!binary |
<LICENSE_KEY>
Enable license in values file
- License name (metadata.name) must match the secretName in the values file
license:
secretName: cfy-license
Apply created config map:
$ kubectl apply -f license.yaml
Add the cloudify-helm repo
Add the cloudify-helm chart repo or upgrade it
$ helm repo add cloudify-helm https://cloudify-cosmo.github.io/cloudify-helm
or
$ helm repo update cloudify-helm
If you want to customize the values it’s recommended to do so before installing the chart - see configuration options below, and either way make sure to review the values file.
Enable PostgreSQL and RabbitMQ deployment
For now deploy PostgreSQL and RabbitMQ as dependent subcharts disabled by default for backward compatibility, so for new deployment you need to enable them.
To do that please ensure you have following parameters in the values file:
postgresql:
deploy: true
rabbitmq:
deploy: true
(optional) If you want to use k8s secrets for store passwords
PostgreSQL initial password
Create k8s secret:
$ kubectl -n NAMESPACE create secret generic SECRET_NAME --from-literal=postgresql-password='POSTGRESQL_INIT_PASSWORD'
Update following parameters in your helm values file:
db:
serverExistingPasswordSecret: "SECRET_NAME"
postgresql:
existingSecret: "SECRET_NAME"
PostgreSQL application connection password
Create k8s secret:
$ kubectl -n NAMESPACE create secret generic SECRET_NAME --from-literal=postgresql-cloudify-password='POSTGRESQL_CLOUDIFY_PASSWORD'
Update following parameters in your helm values file:
db:
cloudifyExistingPassword:
secret: "SECRET_NAME"
RabitMQ password
Create k8s secret:
$ kubectl -n NAMESPACE create secret generic SECRET_NAME --from-literal=rabbitmq-password='RABBITMQ_PASSWORD' --from-literal=rabbitmq-erlang-cookie='RABBITMQ_ERLANG_COOKIE'
Update following parameters in your helm values file:
queue:
existingPasswordSecret: "SECRET_NAME"
rabbitmq:
auth:
existingPasswordSecret: "SECRET_NAME"
existingErlangSecret: "SECRET_NAME"
Cloudify Manager worker admin password
Create k8s secret:
$ kubectl -n NAMESPACE create secret generic SECRET_NAME --from-literal=cfy-admin-password='CLOUDIFY_ADMIN_PASSWORD'
Update following parameters in your helm values file:
config:
security:
existingAdminPassword:
secret: "SECRET_NAME"
(optional) Ensure UI access to the manager upon installation
[OPTION 1]
Use ingress-controller (e.g. NGINX Ingress Controller - https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx/deploy/)
HTTP
- Modify Ingress section accordingly (see example):
ingress: enabled: true host: cloudify-manager.DOMAIN annotations: kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-body-size: 50m # use this annotation to allow upload of resources up to 50mb (e.g. plugins) # cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: "letsencrypt-prod" # use this annotation to utilize an installed cert-manager tls: enabled: false secretName: cfy-secret-nameHTTPS - Pre-applied SSL Cert
- Create SSL secret with tls certificate
apiVersion: v1 kind: Secret metadata: name: cfy-secret-name namespace: NAMESPACE data: tls.crt: SSL_TLS_CRT tls.key: SSL_TLS_KEY type: kubernetes.io/tls - Modify Ingress section accordingly (see example):
ingress: enabled: true host: cloudify-manager.DOMAIN annotations: kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-body-size: 50m # use this annotation to allow upload of resources up to 50mb (e.g. plugins) # cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: "letsencrypt-prod" # use this annotation to utilize an installed cert-manager tls: enabled: true secretName: cfy-secret-nameHTTPS - Certificate Manager
- Use certificate manager (e.g. Let’s Encrypt via cert-manager - https://cert-manager.io/docs/)
- Modify Ingress section accordingly (see example):
ingress: enabled: true host: cloudify-manager.DOMAIN annotations: kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-body-size: 50m # use this annotation to allow upload of resources up to 50mb (e.g. plugins) cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: "<cluster-issuer-name>" # use this annotation to utilize an installed cert-manager tls: enabled: true secretName: cfy-secret-name **HTTP/HTTPS options will expose Cloudify Manager UI on a URL matching the `host` value**
[OPTION 2]
Skip Ingress and expose the Cloudify Manager service using LoadBalancer.
To have a fixed URL, you must utilize a DNS service to route the LB URL (hostname) to the URL you want.
HTTP
For this method you need to edit the Service section to use the right type:
service:
host: cloudify-manager-worker
type: LoadBalancer
name: cloudify-manager-worker
http:
port: 80
https:
port: 443
internal_rest:
port: 53333
That will create a load balancer depending on your K8S infrastructure (e.g. EKS will create a Classic Load Balancer).
Also please add parameter config.public_ip with DNS name which you are going to configure for you Cloudify Manager load balancer endpoint, for example:
config:
public_ip: cloudify-manager.example.com
To get the hostname of the load balancer run:
$ kubectl describe svc/cloudify-manager-worker -n NAMESPACE | grep Ingress
Then you can configure DNS record (ALIAS type), points to this load balancer hostname.
The value of the ingress will be the UI URL of the Cloudify Manager.
HTTPS
- To secure the site with SSL you can update the load balancer configuration to utilize an SSL Certificate
After values are verified, install the manager worker chart
$ helm install cloudify-manager-worker cloudify-helm/cloudify-manager-worker --version 0.4.0 -f ./cloudify-manager-worker/values.yaml -n NAMESPACE
Configuration options of cloudify-manager-worker values.yaml
| Key | Type | Default | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| additionalSecrets | object | {} |
Additional secrets to mount on the manager worker pod, make sure the ‘name’ is also the secret name in the cluster. uncomment secrets and define your mounts More than one secret can be added and more than one mount+sub Path can defined for each secret. (below is an example), . secrets need to be base64 encoded | |
| auth | object | object | Parameters group for auth (for CM worker version >= 7.0) | |
| auth.afterLogoutUrl | string | "/console/login" |
After logout page URL | |
| auth.certPath | string | "" |
Path to SSL certificate | |
| auth.loginPageUrl | string | "/console/login" |
Login page URL | |
| auth.type | string | "local" |
Auth type | |
| config | object | object | Parameters group for Cloudify Manager configuration | |
| config.after_bash | string | "" |
bash commands for execute after main startup script | |
| config.caCertPath | string | "/mnt/cloudify-data/ssl/ca.crt" |
Path to CA certificate. | |
| config.cliLocalProfileHostName | string | "localhost" |
“manager.cli_local_profile_host_name” parameter from Cloudify Manager config.yaml file. | |
| config.labels | object | {} |
Add labels to Manager-worker container (see example below). example-label: “cloudify-example” | |
| config.mgmtWorkerCount | int | 8 |
Maximum number of worker processes started by the management worker. | |
| config.minReadySeconds | int | 120 |
Minimum number of seconds for which a newly created Pod should be running and ready without any of its containers crashing, for it to be considered available. | |
| config.private_ip | string | nil |
“manager.private_ip” parameter from Cloudify Manager config.yaml file. If is not set, will be calculated automatically. | |
| config.public_ip | string | nil |
“manager.public_ip” parameter from Cloudify Manager config.yaml file. If is not set, will be calculated automatically. | |
| config.replicas | int | 1 |
Replicas count for launch. Multiple replicas works only with NFS like volume. | |
| config.security.adminPassword | string | "admin" |
Initial admin password for Cloudify Manager. | |
| config.security.existingAdminPassword.key | string | "cfy-admin-password" |
Name of existing k8s secret key with initial password for Cloudify Manager admin user. | |
| config.security.existingAdminPassword.secret | string | "" |
Name of existing k8s secret with initial password for Cloudify Manager admin user. If not empty, existing secret will be used instead of config.security.adminPassword parameter. | |
| config.security.sslEnabled | bool | false |
Enable SSL for Cloudify Manager. | |
| config.startDelay | int | 0 |
Delay before Cloudify Manager start, in seconds | |
| config.tlsCertPath | string | "/mnt/cloudify-data/ssl/tls.crt" |
Path to TLS certificate. | |
| config.tlsKeyPath | string | "/mnt/cloudify-data/ssl/tls.key" |
Path to TLS certificate key. | |
| config.userConfig.loginHint | bool | true |
Enable initial login password hint. | |
| config.userConfig.maxBodySize | string | "2gb" |
Maximum manager forwarded request size. | |
| config.workerCount | int | 4 |
Cloudify Manager worker count. Suggested worker count for 1vcpu manager, add more if using a stronger host | |
| containerSecurityContext | object | object | Parameters group for k8s containers security context | |
| db | object | object | Parameters group for connection to PostgreSQL database | |
| db.cloudifyDBName | string | "cloudify_db" |
Database name for store Cloudify Manager data | |
| db.cloudifyExistingPassword.key | string | "postgresql-cloudify-password" |
Name of existing k8s secret key with PostgreSQL application connection password. | |
| db.cloudifyExistingPassword.secret | string | "" |
Name of existing k8s secret with PostgreSQL application connection password. If not empty, existing secret will be used instead of db.cloudifyPassword parameter. | |
| db.cloudifyPassword | string | "cloudify" |
Password for DB connection | |
| db.cloudifyUsername | string | "cloudify" |
Username for DB connection | |
| db.host | string | "postgres-postgresql" |
PostgreSQL connection host. If db.useExternalDB == true this value should contain FQDN, otherwise hostname without k8s domain. | |
| db.postgresqlSslClientVerification | bool | true |
Enable PostgreSQL client SSL certificate verification. | |
| db.serverDBName | string | "postgres" |
Database name for initial connection | |
| db.serverExistingPasswordSecret | string | "" |
Name of existing k8s secret with PostgreSQL initial connection password (must contain a value for postgresql-password key). If not empty, existing secret will be used instead of db.serverPassword parameter. |
|
| db.serverPassword | string | "cfy_test_pass" |
Password for initial DB connection | |
| db.serverUsername | string | "postgres" |
Username for initial DB connection | |
| db.useExternalDB | bool | false |
When switched to true, it will take the FQDN for the pgsql database in host, and require CA cert in secret inputs under TLS section | |
| fullnameOverride | string | "cloudify-manager-worker" |
||
| hotfix | object | {"rnd1267":true} |
Parameters group for enabling hotfixes/patches for various issues | |
| hotfix.rnd1267 | bool | true |
Hotfix for RND-1267: in the 7.0.x branch, on some k8s setups, the manager can’t be installed and throws a “/tmp/tmp |
|
| image | object | object | Parameters group for Docker images | |
| image.pullPolicy | string | "IfNotPresent" |
Specify a imagePullPolicy, Defaults to ‘Always’ if image tag is ‘latest’, else set to ‘IfNotPresent’. ref: http://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/images/#pre-pulling-images | |
| image.pullSecrets | list | [] |
Optionally specify an array of imagePullSecrets. Secrets must be manually created in the namespace. ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/pull-image-private-registry/ | |
| image.repository | string | "cloudifyplatform/premium-cloudify-manager-worker" |
Docker image repository | |
| image.tag | string | "6.4.0" |
Docker image tag | |
| ingress | object | object | Parameters group for ingress (managed external access to service) | |
| ingress.annotations | object | object | Ingress annotation object. Please see an example in values.yaml file | |
| ingress.enabled | bool | false |
Enable ingress | |
| ingress.host | string | "cfy-efs-app.eks.cloudify.co" |
Hostname for ingress connection | |
| ingress.tls | object | object | Ingress TLS parameters | |
| ingress.tls.enabled | bool | false |
Enabled TLS connections for Ingress | |
| ingress.tls.secretName | string | "cfy-secret-name" |
k8s secret name with TLS certificates for ingress | |
| initContainers | object | object | Parameters group for init containers | |
| initContainers.prepareConfigs.pullPolicy | string | "IfNotPresent" |
imagePullPolicy for prepare-configs init container | |
| initContainers.prepareConfigs.repository | string | "busybox" |
Docker image repository for prepare-configs init container | |
| initContainers.prepareConfigs.resources | object | object | resources requests and limits for prepare-configs init container | |
| initContainers.prepareConfigs.resources.requests | object | {"cpu":0.1,"memory":"50Mi"} |
requests for prepare-configs init container | |
| initContainers.prepareConfigs.tag | string | "1.34.1-uclibc" |
Docker image tag for prepare-configs init container | |
| initContainers.waitDependencies.enabled | bool | true |
Enable wait-for-dependencies init container | |
| initContainers.waitDependencies.pullPolicy | string | "IfNotPresent" |
imagePullPolicy for wait-for-dependencies init container | |
| initContainers.waitDependencies.repository | string | "busybox" |
Docker image repository for wait-for-dependencies init container | |
| initContainers.waitDependencies.resources | object | object | resources requests and limits for wait-for-dependencies init container | |
| initContainers.waitDependencies.resources.requests | object | {"cpu":0.1,"memory":"50Mi"} |
requests for wait-for-dependencies init container | |
| initContainers.waitDependencies.tag | string | "1.34.1-uclibc" |
Docker image tag for wait-for-dependencies init container | |
| initContainers.waitDependencies.timeout | string | "10m" |
timeout for waiting when all dependencies up | |
| kubeVersion | string | "" |
||
| license | object | {} |
Can contain “secretName” field with existing license in k8s configMap, to use Secret instead, set useSecret to true. | |
| livenessProbe | object | object | Parameters group for pod liveness probe | |
| livenessProbe.enabled | bool | true |
Enable liveness probe | |
| livenessProbe.failureThreshold | int | 8 |
liveness probe failure threshold | |
| livenessProbe.httpGet.path | string | "/api/v3.1/ok" |
liveness probe HTTP GET path | |
| livenessProbe.initialDelaySeconds | int | 600 |
liveness probe initial delay in seconds | |
| livenessProbe.periodSeconds | int | 30 |
liveness probe period in seconds | |
| livenessProbe.successThreshold | int | 1 |
liveness probe success threshold | |
| livenessProbe.timeoutSeconds | int | 15 |
liveness probe timeout in seconds | |
| mainConfig | string | config.yaml template | Content of the main configuration file for cloudify manager (config.yaml). | |
| nameOverride | string | "cloudify-manager-worker" |
||
| nodeSelector | object | {} |
Node labels for default backend pod assignment. Ref: https://kubernetes.io/docs/user-guide/node-selection/ | |
| okta | object | object | Parameters group for OKTA (for CM worker version < 7.0) | |
| okta.certPath | string | "" |
SSL certificate path | |
| okta.enabled | bool | false |
Enable OKTA support. | |
| okta.portalUrl | string | "" |
Portal URL | |
| okta.secretName | string | "okta-license" |
k8s secret name containing the OKTA certificates. | |
| okta.ssoUrl | string | "" |
SSO URL | |
| podAnnotations | object | {} |
Additional annotations for Cloudify Manager Worker pods. | |
| podSecurityContext | object | object | Parameters group for k8s pod security context | |
| postgresql | object | object | Parameters group for bitnami/postgresql helm chart. Details: https://github.com/bitnami/charts/blob/main/bitnami/postgresql/README.md | |
| queue | object | object | Parameters group for connection to RabbitMQ (Message Broker) | |
| queue.existingPasswordSecret | string | "" |
Name of existing k8s secret with RabbitMQ password (must contain a value for rabbitmq-password key). If not empty, existing secret will be used instead of queue.password parameter. |
|
| queue.host | string | "rabbitmq" |
RabbitMQ connection host (without k8s domain) | |
| queue.password | string | "cfy_test_pass" |
Password for connection to RabbitMQ | |
| queue.username | string | "cfy_user" |
Username for connection to RabbitMQ | |
| rabbitmq | object | object | Parameters group for bitnami/rabbitmq helm chart. Details: https://github.com/bitnami/charts/blob/main/bitnami/rabbitmq/README.md | |
| readinessProbe | object | object | Parameters group for pod readiness probe | |
| readinessProbe.enabled | bool | true |
Enable readiness probe | |
| readinessProbe.failureThreshold | int | 2 |
readiness probe failure threshold | |
| readinessProbe.httpGet.path | string | "/console" |
readiness probe HTTP GET path | |
| readinessProbe.initialDelaySeconds | int | 0 |
readiness probe initial delay in seconds | |
| readinessProbe.periodSeconds | int | 10 |
readiness probe period in seconds | |
| readinessProbe.successThreshold | int | 2 |
readiness probe success threshold | |
| readinessProbe.timeoutSeconds | int | 5 |
readiness probe timeout in seconds | |
| resources | object | object | Parameters group for resources requests and limits | |
| resources.limits | object | {"cpu":3,"memory":"4.5Gi"} |
resources limits for Cloudify Manager container | |
| resources.requests | object | {"cpu":0.5,"memory":"2Gi"} |
resources requests for Cloudify Manager container | |
| service | object | object | Parameters group for k8s service | |
| service.extraPorts | object | {} |
k8s service additional ports. If you need to open additional ports for the manager, uncomment extraPorts and define your port parameters - More than one can be added (below is an example). | |
| service.host | string | "cloudify-manager-worker" |
k8s service host | |
| service.http.port | int | 80 |
k8s service http port | |
| service.https.port | int | 443 |
k8s service https port | |
| service.internalRest.port | int | 53333 |
k8s service internal rest port | |
| service.name | string | "cloudify-manager-worker" |
k8s service name | |
| service.type | string | "ClusterIP" |
k8s service type | |
| serviceAccount | string | nil |
Name of the serviceAccount for attach to Cloudify Manager Worker pods. | |
| startupProbe | object | object | Parameters group for pod startup probe | |
| startupProbe.enabled | bool | true |
Enable startup probe | |
| startupProbe.failureThreshold | int | 30 |
startup probe failure threshold | |
| startupProbe.httpGet.path | string | "/console" |
startup probe HTTP GET path | |
| startupProbe.initialDelaySeconds | int | 30 |
startup probe initial delay in seconds | |
| startupProbe.periodSeconds | int | 10 |
startup probe period in seconds | |
| startupProbe.successThreshold | int | 1 |
startup probe success threshold | |
| startupProbe.timeoutSeconds | int | 5 |
startup probe timeout in seconds | |
| tls.certManager | object | {"caSecretName":"cfy-ca-tls","expiration":"87660h","generate":false} |
Parameters sub-group for generate certificates using cert-manager. | |
| tls.certManager.caSecretName | string | "cfy-ca-tls" |
Secret name for CA certificate (necessary only for generate certificates by cert-manager). | |
| tls.certManager.expiration | string | "87660h" |
Expiry time for generated certs (87660h = 10y). | |
| tls.certManager.generate | bool | false |
Enable to auto create certs using cert-manager. | |
| tls.pgsqlSslCaName | string | "postgres_ca.crt" |
subPath name for ssl CA cert in k8s secret. Required only for connection to external PostgreSQL database. | |
| tls.pgsqlSslCertName | string | "" |
subPath name for ssl certificate in k8s secret for connection to external PostgreSQL database. Isn’t required if db.postgresqlSslClientVerification = false. | |
| tls.pgsqlSslKeyName | string | "" |
subPath name for ssl key in k8s secret for connection to external PostgreSQL database. Isn’t required if db.postgresqlSslClientVerification = false. | |
| tls.pgsqlSslSecretName | string | "pgsql-external-cert" |
k8s secret name with ssl certificates for external PostgreSQL database. Required only for connection to external PostgreSQL database. | |
| tls.secretName | string | "cfy-certs" |
k8s secret name with certificates to secure communications between cloudify manager and postgresql | rabbitmq deployed inside the same k8s cluster. |
| userConfig | string | userConfig.json template | Content of the userConfig.json configuration file | |
| volume | object | object | Parameters group for data storage volume For multiple replicas of cloudify manager use NFS like storage, storageClass: ‘cm-efs’ (AWS example), accessMode: ‘ReadWriteMany’ Single replica - EBS (AWS example), storageClass: ‘gp2’ (AWS example), accessMode: ‘ReadWriteOnce’ | |
| volume.accessMode | string | "ReadWriteOnce" |
volume access mode | |
| volume.size | string | "3Gi" |
volume size | |
| volume.storageClass | string | "gp2" |
volume storage class |
Edit the values file in ./cloudify-manager-worker/values.yaml according to your preferences:
Upgrade cloudify manager worker
To upgrade cloudify manager use ‘helm upgrade’.
For example to change to newer version (e.g. from 6.2.0 to 6.3.0 in this example),
Change image version in values.yaml:
Before:
image:
repository: cloudifyplatform/premium-cloudify-manager-worker
tag: 6.2.0
After:
image:
repository: cloudifyplatform/premium-cloudify-manager-worker
tag: 6.3.0
Run ‘helm upgrade’
$ helm upgrade cloudify-manager-worker cloudify-helm/cloudify-manager-worker -f ./cloudify-manager-worker/values.yaml -n NAMESPACE
If DB schema was changed in newer version, needed migration will be running first on DB, then application will be restarted during upgrade - be patient, because it may take a couple of minutes.
Upgrading to Cloudify manager worker 7.X [UNRELEASED]
In Cloudify Manager 7 we upgraded the version of PostgreSQL to 14 and of RabbitMQ to 3.10.
In Cloudify-Helm we use the bitnami/postgresql chart (which deploys PostgreSQL version 11 for Cloudify Manager 6.X, also compatible with Cloudify Manager 7.X). The bitnami/postgresql chart does not support database version upgrade, so if the user likes to upgrade PostgreSQL they’ll need to do so manually using the pg_upgrade tool.
Additionally, coming from Cloudify Manager 6.X, the
populate_deployment_statuses and migrate_pickle_to_json scripts must run
on the data in the Manager’s database in order to use it in the new version.
It is handled in the config.after_bash value.
Change the following in values.yaml:
image:
repository: cloudifyplatform/premium-cloudify-manager-worker
tag: 7.0.0
---
rabbitmq:
image:
tag: 3.10.13-debian-11-r9
---
config:
after_bash: "if [[ $(/opt/manager/env/bin/python --version) == *'3.10'* ]]; then opt/manager/env/bin/python /opt/mgmtworker/env/lib/python3.10/site-packages/cloudify_system_workflows/snapshots/populate_deployment_statuses.py; opt/manager/env/bin/python /opt/mgmtworker/env/lib/python3.10/site-packages/cloudify_system_workflows/snapshots/migrate_pickle_to_json.py; fi"
Alternatively these can be set directly through the helm upgrade command
(notice the --set of the erlang cookie, see above):
$ helm upgrade cloudify-manager-worker cloudify-helm/cloudify-manager-worker \
--reuse-values --set image.tag=7.0.0 --set rabbitmq.image.tag='3.10.13-debian-11-r9' \
--set config.after_bash="if [[ \$(/opt/manager/env/bin/python --version) == *'3.10'* ]]; then opt/manager/env/bin/python /opt/mgmtworker/env/lib/python3.10/site-packages/cloudify_system_workflows/snapshots/populate_deployment_statuses.py; opt/manager/env/bin/python /opt/mgmtworker/env/lib/python3.10/site-packages/cloudify_system_workflows/snapshots/migrate_pickle_to_json.py; fi" \
--set rabbitmq.auth.erlangCookie=$RABBITMQ_ERLANG_COOKIE -n NAMESPACE
Image:
image:
repository: "cloudifyplatform/premium-cloudify-manager-worker"
tag: "6.3.0"
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
DB - postgreSQL:
db:
useExternalDB: false # when switched to true, it will take the FQDN for the pgsql database in host, and require CA cert in secret inputs under TLS section
postgresqlSslClientVerification: true
host: postgres-postgresql
cloudify_db_name: "cloudify_db"
cloudify_username: "cloudify"
cloudify_password: "cloudify"
server_db_name: "postgres"
server_username: "postgres"
server_password: "cfy_test_pass"
Message Broker - rabbitmq:
queue:
host: rabbitmq
username: "cfy_user"
password: "cfy_test_pass"
Service:
See customization example above
service:
host: cloudify-manager-worker
type: ClusterIP
name: cloudify-manager-worker
http:
port: 80
https:
port: 443
internal_rest:
port: 53333
node selector - select on which nodes cloudify manager may run:
nodeSelector: {}
# nodeSelector:
# nodeType: onDemand
Secrets for TLS/SSL certificates
tls:
# certificates as a secret, to secure communications between cloudify manager and postgress|rabbitmq
secretName: cfy-certs
# Parameters for PostgreSQL SSL certificates, required for external postgresql database only
pgsqlSslSecretName: pgsql-external-cert # k8s secret name with psql ssl certs
pgsqlSslCaName: postgres_ca.crt # subPath name for ssl CA cert in k8s secret
pgsqlSslCertName: "" # subPath name for ssl cert in k8s secret, isn't required
pgsqlSslKeyName: "" # subPath name for ssl key in k8s secret, isn't required
Additional secrets to mount onto cloudify-manager-worker pod
In case you need to mount additional secrets to the pod (e.g. self-signed certificate for 3rd party connection) For each secret you need to define its mounts. It’s possible to mounts several files under one secret definition using different subPaths See below or example in the values file.
additionalSecrets:
- name: secretName
mounts:
- mountPath: /mnt/cloudify-data/ssl/secretName.crt
subPath: secretName.crt
- mountPath: /mnt/cloudify-data/ssl/secretName.key
subPath: secretName.key
resources requests and limits:
resources:
requests:
memory: 0.5Gi
cpu: 0.5
Persistent volume size for EBS/EFS:
If using multiple replicas (High availability), NFS like Storage like EFS must be used. For more details see links to different cloud providers here
volume:
storage_class: "efs"
access_mode: "ReadWriteMany"
size: "3Gi"
If using one replicas, you can use EBS (gp2) for example, gp2 is default:
volume:
storage_class: "gp2"
access_mode: "ReadWriteOnce"
size: "3Gi"
readiness probe may be enabled/disabled
readinessProbe:
enabled: true
path: /console
initialDelaySeconds: 10
NOTE: If you need to deploy Cloudify Manager in high availability mode with 2 replicas (config.replicas=2), and your k8s cluster version < 1.25 please set value for parameter readinessProbe.initialDelaySeconds to 120 for avoid issues with second replica start.
Config
You can delay start of cfy manager / install all plugins / disable security (not recommended)…
config:
start_delay: 0
# Multiple replicas works only with EFS(NFS) volume
replicas: 1
install_plugins: false
cli_local_profile_host_name: localhost
security:
ssl_enabled: false
admin_password: admin
tls_cert_path: /mnt/cloudify-data/ssl/tls.crt
tls_key_path: /mnt/cloudify-data/ssl/tls.key
ca_cert_path: /mnt/cloudify-data/ssl/ca.crt
Ingress
You may enable ingress-nginx and generate automatically cert if you have ingress-nginx / cert-manager installed (e.g. using nginx with existing ssl secret) - See above for more details
ingress:
enabled: false
host: cloudify-manager.app.cloudify.co
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-body-size: 50m # use this annotation to allow upload of resources up to 50mb (e.g. plugins)
# cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: "letsencrypt-prod" # use this annotation to utilize an installed cert-manager
tls:
enabled: false
secretName: cfy-secret-name
If you have parameter config.security.sslEnabled set to “true”, you need configure ingress for use HTTPS backend protocol. In case of nginx ingress, you need to add additional annotation “nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-protocol” set to “HTTPS”, so in your values file it should looks like:
ingress:
enabled: true
host: cloudify-manager.app.cloudify.co
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-protocol: "HTTPS"
Create secret for okta-license - required if using Okta/SSO
First obtain the okta/sso server certificate and store it in a file for exanple okta_certificate.pem
echo -n '-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
MIIDXDCCAkSgAwIBAgIJAKwO13ndNBPjMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBCwUAMCkxJzAlBgNV
BAMMHkNsb3VkaWZ5IGdlbmVyYXRlZCBjZXJ0aWZpY2F0ZTAeFw0yMTA2MTQxMjMx
NDZaFw0zMTA2MTIxMjMxNDZaMCYxJDAiBgNVBAMMG2lwLTEwLTEwLTQtMTE2LmVj
-----END CERTIFICATE-----' > ./okta_certificate.pem
then let’s create the okta-license secret in the NAMESPACE
kubectl create secret generic okta-license --from-file=./okta_certificate.pem -n NAMESPACE
Troubleshoot
Some common use cases:
License is not uploaded correctly upon installation
[deprecated] This might happen if the English convention of licence/license is not alligned across the values (name of the value and its value), or across the license/licence configMap.
Since v0.4.1 licence convention is not supported. please use license.
The StatefulSet accepts a secret/configMap with the data value of this syntax cfy_license.yaml
After ensuring the above, try to reinstall the worker chart
- Workaround for this issue would be to manually upload the license after the manager installation through the UI after logging in or via the CLI.
Cloudify Manager installation succeded but I can’t reach the UI
Please see above
If you already installed the chart, update the values accordingly and run:
$ helm upgrade cloudify-manager-worker cloudify-helm/cloudify-manager-worker -f <path-to-values.yaml-file> -n NAMESPACE
I had to reinstall the worker chart and now it fails on installation
This might happen due to inter-communications between the components in the different pods, a work around for that would be to delete the postgresql (has a PersistentVolume) and the rabbitmq pods, which will trigger a restart for them.
$ kubectl delete pod postgres-postgresql-0 -n NAMESPACE
$ kubectl delete pod rabbitmq-0 -n NAMESPACE
Then try reinstalling the worker chart.
Can’t find the help you need here?
Feel free to open an issue in the helm chart GitHub page, or contact us through our website.
Uninstallation
Uninstall helm release:
$ helm uninstall cloudify-manager-worker -n NAMESPACE
If you want to remove Persistent Volume Claims (for example if you are going to reinstall stack without data saving):
kubectl --namespace NAMESPACE delete persistentvolumeclaims cfy-worker-pvc data-postgres-postgresql-0 data-rabbitmq-0
To clean the supporting files:
$ kubectl delete secret cfy-certs -n NAMESPACE
$ kubectl delete secret cfy-ca-tls -n NAMESPACE
$ kubectl delete configmap cfy-license -n NAMESPACE